In this chapter we learned about Virtualization. Very simply it is the emulation of a computer on a physical
system. It also could be of an operating system or an application. Virtualization
offers many advantages such as:
- Efficient
use of resources
- Cost and
energy savings
- Fault and
threat isolation
- Simple
backups, recovery, and replication
However some
disadvantages are:
- Compromised
performance
- Increased
complexity
- Increased
licensing costs
- Single point
of failure
Virtual
networks can consist of virtual machines on a physical server. More common are
networks that combine physical and virtual elements. Virtual network components
include a virtual adapter or vNIC which is required to connect to a network. Virtual
bridges or ports on a switch connect to vNICs with a network, whether virtual
or physical. A virtual switch is a logically defined device that operates at
the data link level to pass frames between nodes. Network connection types
include bridged (physical network
using the host machine NIC), NAT (relies
on the host machine to act as NAT device), and host-only (exchange data with each other and host only).
The text
covers remote access and virtual computing through the following methods:
- Dial-up
Networking
- Remote
access servers
- Remote
access protocols
- Remote
virtual computing
The chapter
speaks to Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) which are wide area networks that are
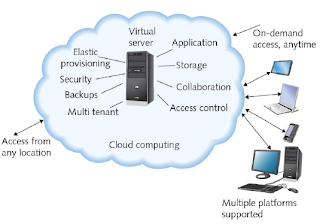
logically defined over public transmission systems. It concludes with cloud
computing (see below) which refers to the flexible provision of data storage, applications,
or services to many clients over a network.
I found the
material to be very informative but yet concise. There were a lot of good
diagrams and illustrations to help make key points.
No comments:
Post a Comment